7: Cretaceous Georgia,
Georgia's Dinosaurs & More
The Cretaceous Period began 145.5 million years ago and ended 65.5 million years ago, it was generally warm to very warm and saw high sea levels.
High sea levels were the norm for this period in Earth's history, but as always, the climate fluctuated and sea levels both rose and fell.
Dinosaurs dominated as the terrestrial animals and are present in Georgia. For most of the Cretaceous, the poles were probably ice free. New groups of mammals, birds and flowering plants emerged and proliferated.
During the long warm phases of global climates, Georgia’s coastline stretched roughly along the modern Fall Line from Columbus, through Macon and on to Augusta.
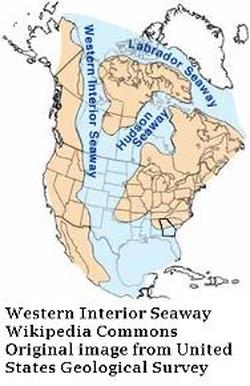
To the west of Georgia and covering most of the Mid-Western United States was the Western Interior Seaway. Georgia sat at a crossroads between the Western Interior Seaway, the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean.
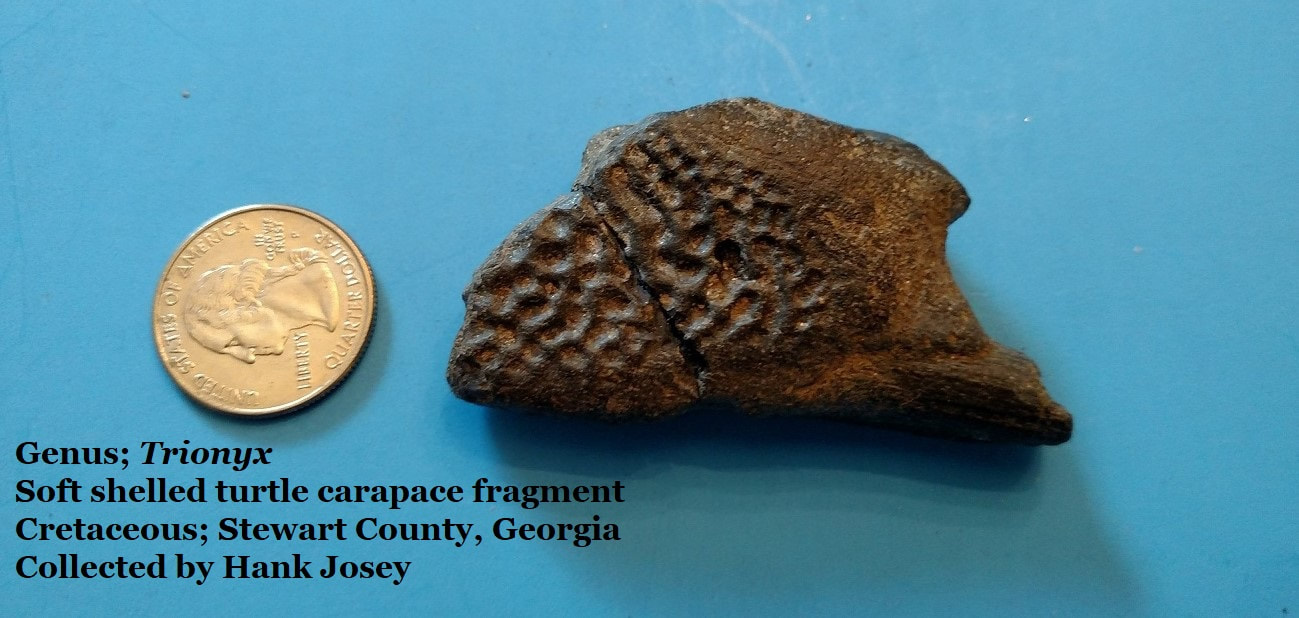
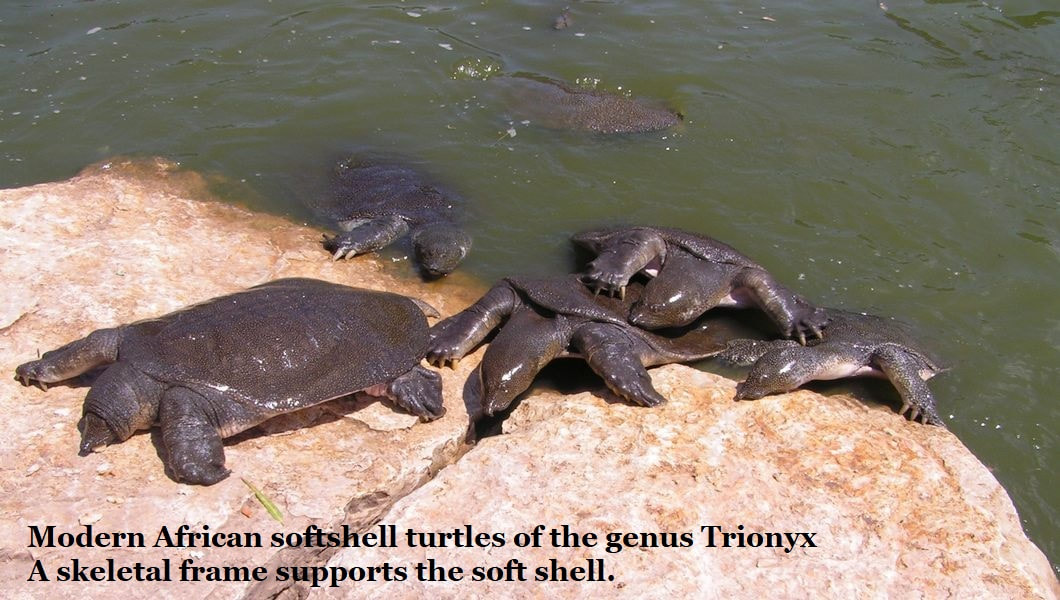
Along this lost Georgia coastline, and in our rivers were turtles, there were huge, terrible crocodiles up to 25 feet long and perhaps capable of taking dinosaurs. The sea covering South Georgia was an equally dangerous place full of large predators including giant reptiles and many species of large sharks and hungry bony fish.
In several West Georgia and East Alabama locations the distinctive oyster Exogyra ponderosa can be collected, sometimes in masses.


